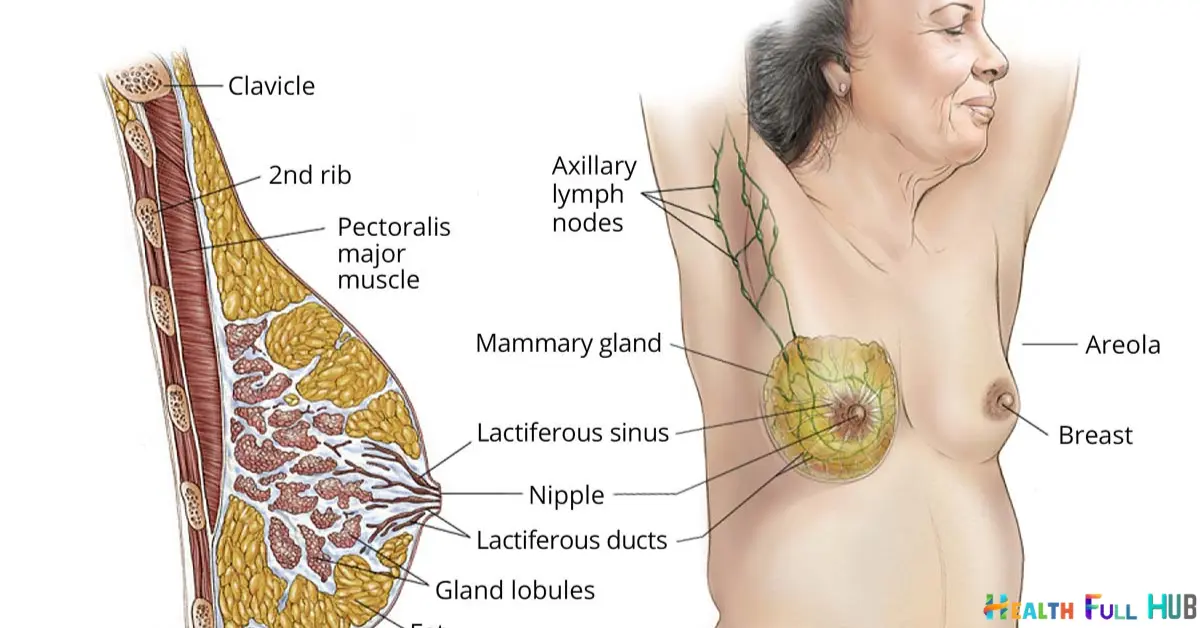
Introduction
What Is Breast Cancer is individual of the most coarse types of tumor worldwide, moving heaps of things each year. It happens when containers in the breast fabric evolve madly, leading to the composition of a cyst. Although it generally affects mothers, brothers can also be pronounced along feelings cancer, though the cases are considerably more precious. With early detection and advances in situation, the durability rates for bosom cancer have revised severely, but it debris a disease that intensely influences patients two together physically and excitedly.
Types
Breast cancer is not a one-size-fits-all diagnosis. Several different types of breast cancer exist, each varying in its nature and treatment options.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS): This is a non-invasive form of breast cancer where abnormal cells are contained within the milk ducts. Although it hasn’t spread beyond the ducts, it can progress into an invasive type if left untreated.
- Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC): IDC is the most common type of breast cancer, making up about 80% of cases. It begins in the milk ducts but spreads into surrounding breast tissue.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC): ILC starts in the lobules (milk-producing glands) and spreads to nearby breast tissue.
- Other rare types: Some less common forms include medullary carcinoma, mucinous carcinoma, and inflammatory breast cancer. These types can behave differently and may require specialized treatment.
Stages of Breast Cancer
Understanding the stage of breast cancer helps determine the severity and spread of the disease.
- Stage 0: This is the non-invasive stage where the cancer is still confined to the breast ducts or lobules (e.g., DCIS).
- Stage 1: Early-stage invasive cancer where the tumor is small and hasn’t spread extensively.
- Stage 2: The cancer is larger or may have spread to a few nearby lymph nodes but hasn’t reached distant parts of the body.
- Stage 3: The cancer is considered regionally advanced, involving more lymph nodes or adjacent areas, like the chest wall.
- Stage 4: Also known as metastatic breast cancer, this is when the cancer has spread to distant organs such as the lungs, liver, or bones.
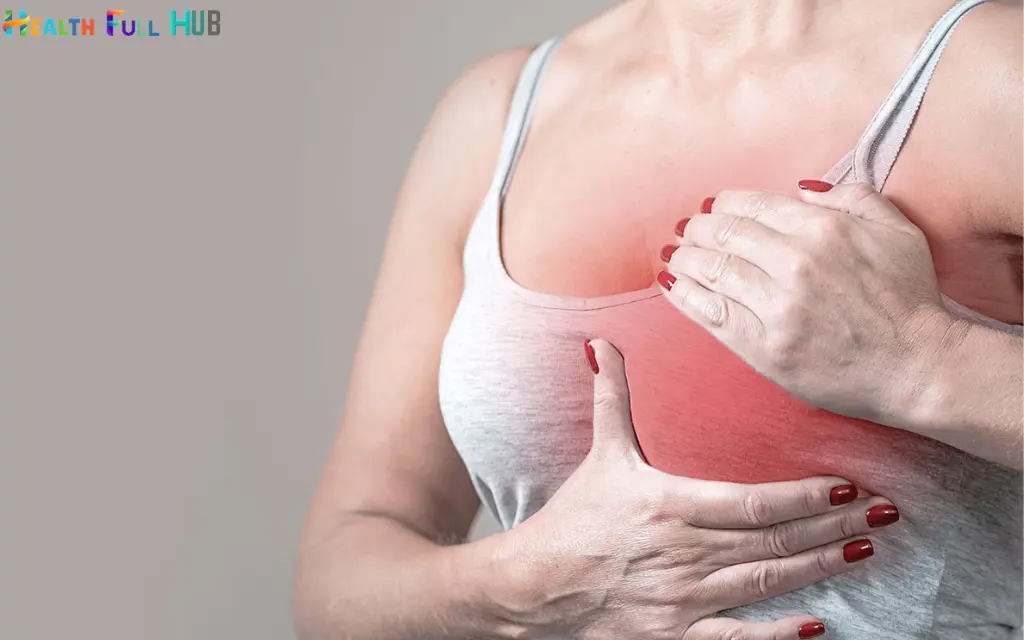
Symptoms
- Physical symptoms: A new lump in the breast or underarm, swelling, skin irritation or dimpling, breast or nipple pain, and changes in nipple appearance.
- Non-physical symptoms: These can include fatigue, unexplained weight loss, or general discomfort, though these are less commonly associated with early detection.
If you notice any unusual changes, it’s critical to see a healthcare provider for a proper evaluation.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing breast cancer, some of which are beyond one’s control.
- Genetic factors: Mutations in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2 are linked to a higher risk of breast and ovarian cancer. If you have a family history of breast cancer, genetic testing may be recommended.
- Lifestyle factors: Alcohol consumption, smoking, obesity, and lack of physical activity are all lifestyle factors that can contribute to breast cancer risk.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to radiation or harmful chemicals can also increase the risk.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing breast cancer usually begins with imaging tests, but a definitive diagnosis requires tissue analysis.
- Mammograms: These are X-ray images of the breast, commonly used for routine screening to detect abnormalities early on.
- Biopsy: If an abnormal area is detected, a biopsy (removal of tissue) is performed to confirm whether cancer is present.
- Genetic testing: For individuals with a strong family history, genetic tests can identify inherited mutations that increase breast cancer risk.
Breast Cancer in Men
Yes, guys can catch breast tumor also, though it’s much rarer. Male feelings malignancy often presents accompanying comparable syndromes, such as a lump or changes in the front of upper body extent. Treatments for men mainly understand the alike protocols as those for daughters, containing surgery, emission, and bomber.
Treatment Options
The treatment for breast cancer depends on the stage, type, and individual health factors. Common treatments include:
- Surgery: The removal of the tumor or the entire breast (mastectomy) may be necessary, depending on the cancer’s size and location.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy beams are used to target and destroy cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: These are drugs that specifically target cancer cells without affecting normal cells.
- Hormone therapy: For cancers that are hormone receptor-positive, hormone-blocking treatments can help slow or stop cancer growth.
The Role of Early Detection
- Self-exams: Performing regular breast self-examinations helps you become familiar with the normal feel of your breasts, making it easier to detect changes.
- Screening programs: Women over a certain age or with high risk should undergo regular mammogram screenings as part of routine health care.
Prevention Strategies
While there’s no guaranteed way to prevent breast cancer, several strategies can reduce your risk.
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a balanced diet, staying physically active, limiting alcohol, and avoiding smoking can help lower the risk.
- Genetic counseling: For those with a family history, speaking with a genetic counselor can help determine your risk and preventive steps, including the possibility of prophylactic (preventive) surgery.
- Diet and exercise: Some studies suggest that a plant-based diet and regular exercise can support overall breast health.
The Emotional Impact
The sensitive toll of heart cancer maybe overpowering. Patients often knowledge worry, despair, and fear. Support networks, whether classification, companions, or breast tumor remains groups, are essential in handling the emotional challenges all the while and afterwards situation.
Life After Breast Cancer
For survivors, life after treatment involves regular monitoring to detect any recurrence. This may include routine scans, blood tests, and physical exams.
- Recovery: Physical rehabilitation, such as exercises to regain strength, is often part of the recovery process.
- Long-term effects: Some treatments have long-term effects, like lymphedema (swelling due to lymph node removal), that need to be managed.
Breast Cancer Awareness and Advocacy
Breast tumor knowledge campaigns have helped sustain innumerable lives by advancing early discovery and raising means for research. From pink tape campaigns to conscience cancer walks, winning complicated can importance